 N O T I C E
N O T I C E 
MSPbots WIKI is moving to a new home at support.mspbots.ai![]() to give you the best experience in browsing our Knowledge Base resources and addressing your concerns. Click here
to give you the best experience in browsing our Knowledge Base resources and addressing your concerns. Click here![]() for more info!
for more info!
 N O T I C E
N O T I C E 
MSPbots WIKI is moving to a new home at support.mspbots.ai![]() to give you the best experience in browsing our Knowledge Base resources and addressing your concerns. Click here
to give you the best experience in browsing our Knowledge Base resources and addressing your concerns. Click here![]() for more info!
for more info!
The API write-back can be customized by configuring the REST API Call bot block. Customizing the API write-back and creating an API REST block enables MSPbots to establish a seamless integration with your systems and allows us to retrieve relevant data so we can create reports that will help you monitor your performance, receive alerts, and perform necessary actions programmatically.
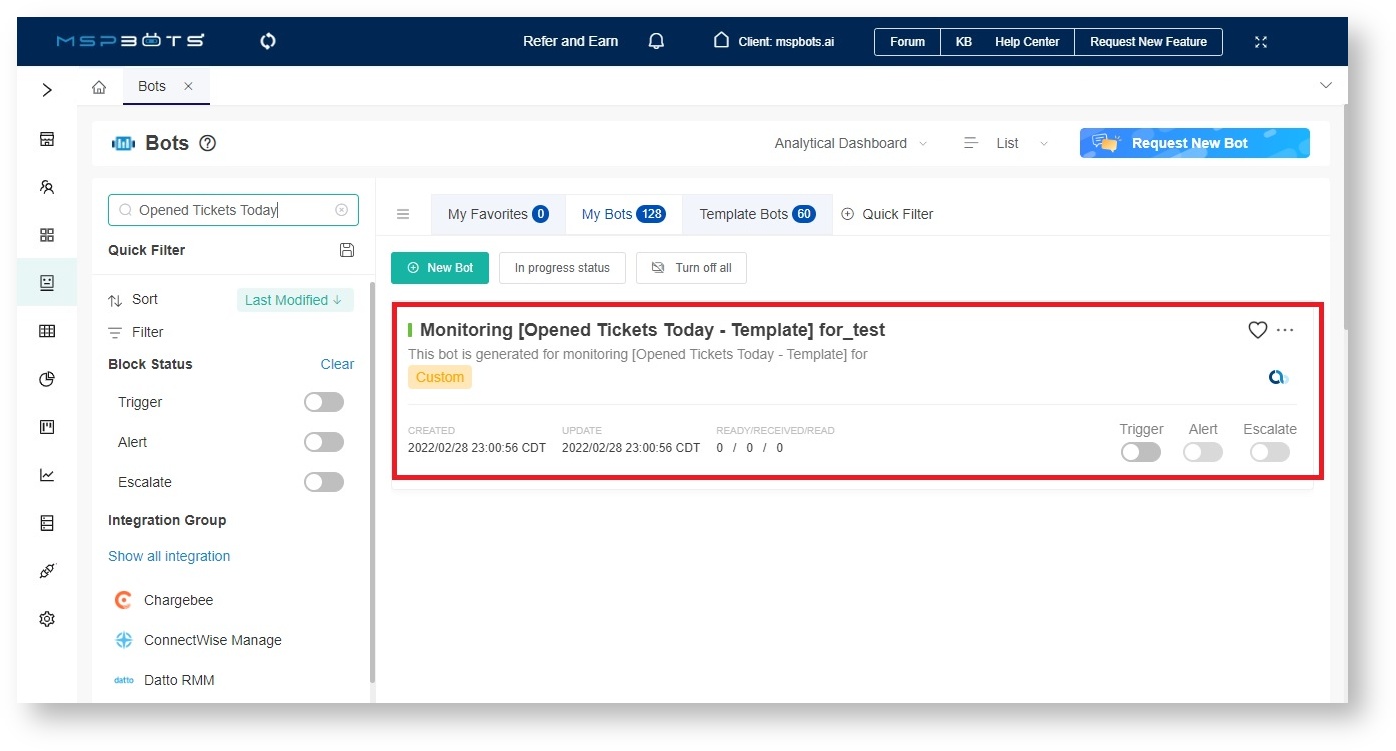
This article is a guide on how to configure the REST API Call bot block. It will use the Monitoring [Opened Tickets Today - Template] for_test bot as an example.
To set up the bot block
- Go to Bots on the MSPbots menu.
- Open the bot that you want to add the REST API Call block to.
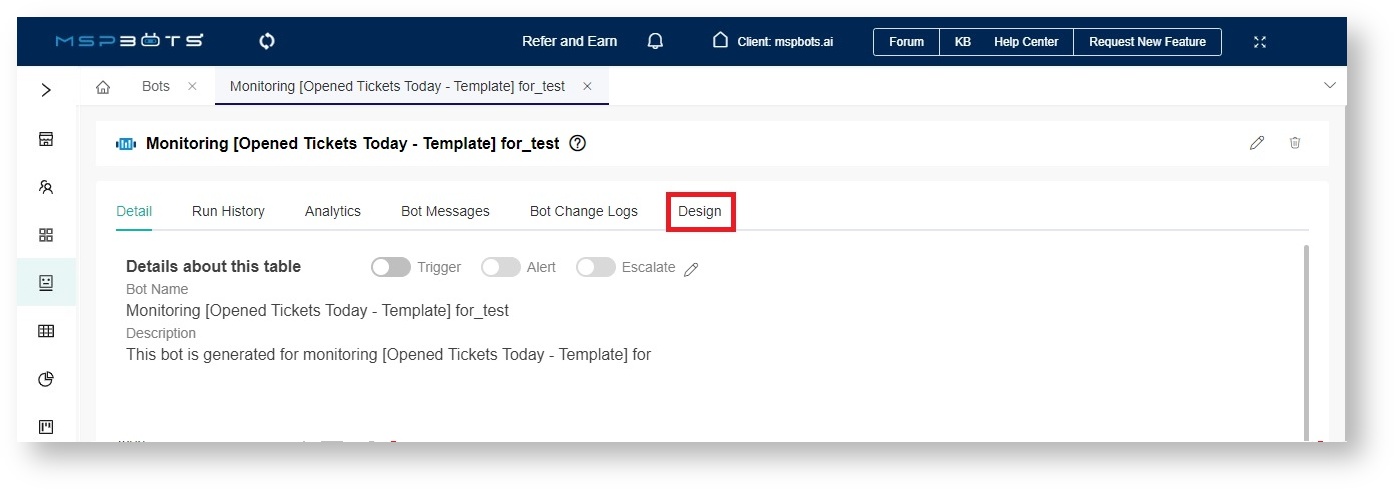
- Go to the Design tab. If a window opens, close it.
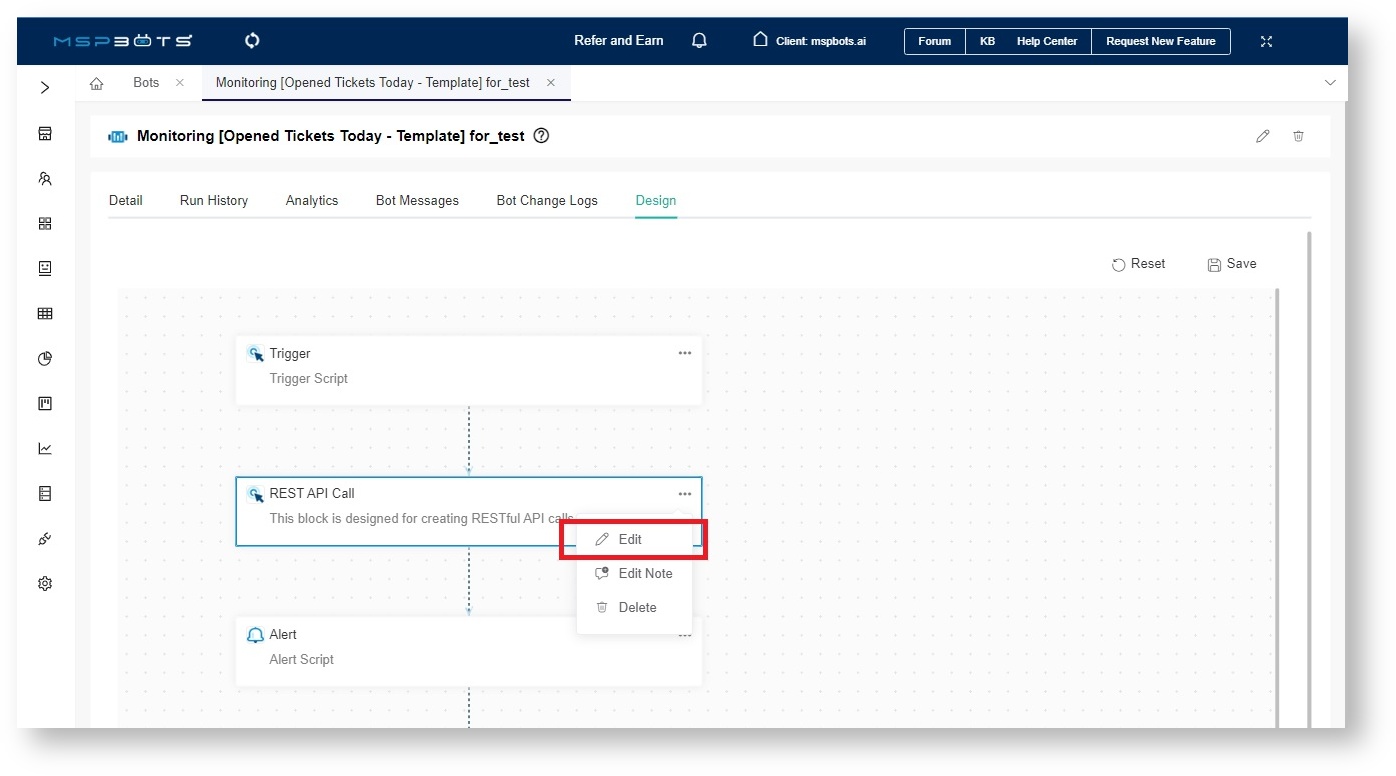
- Hover over the horizontal line between the blocks. Click , select Add a Block, and select the new block.
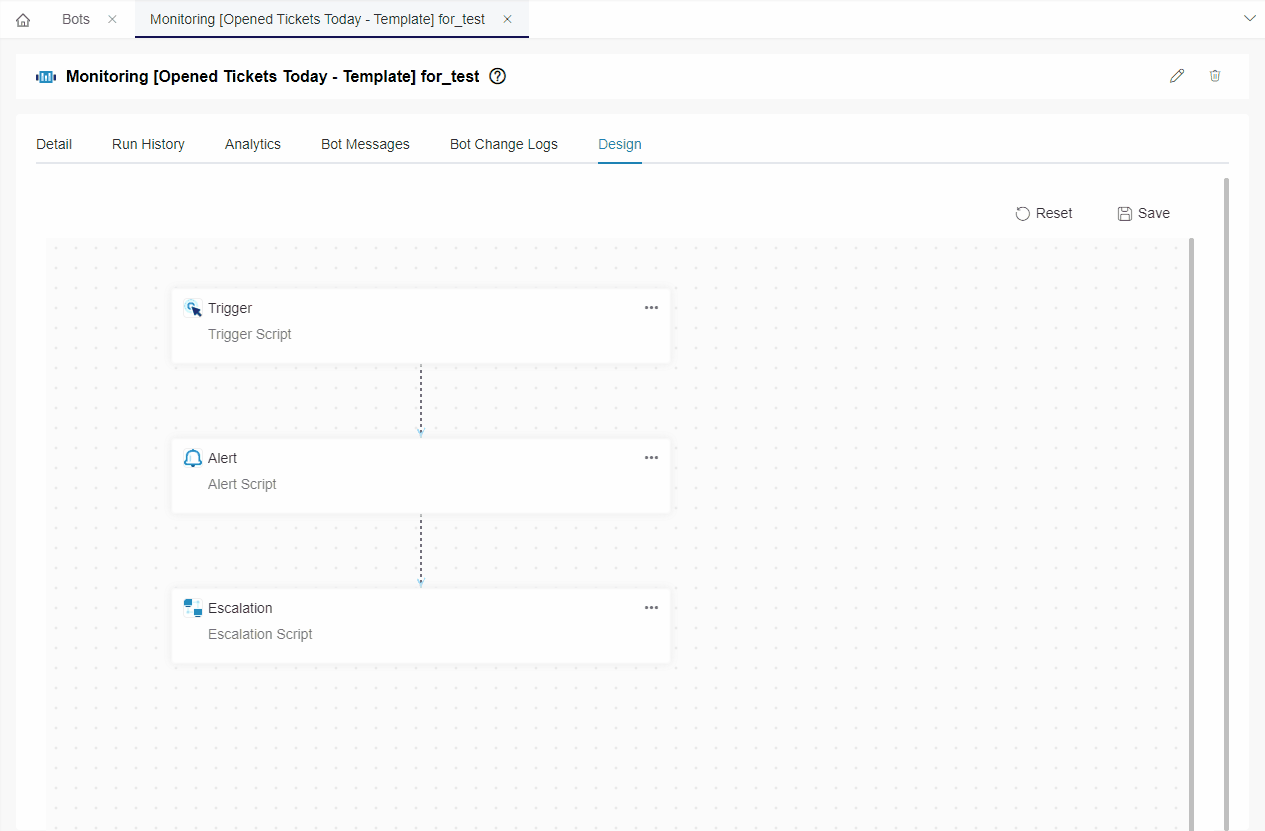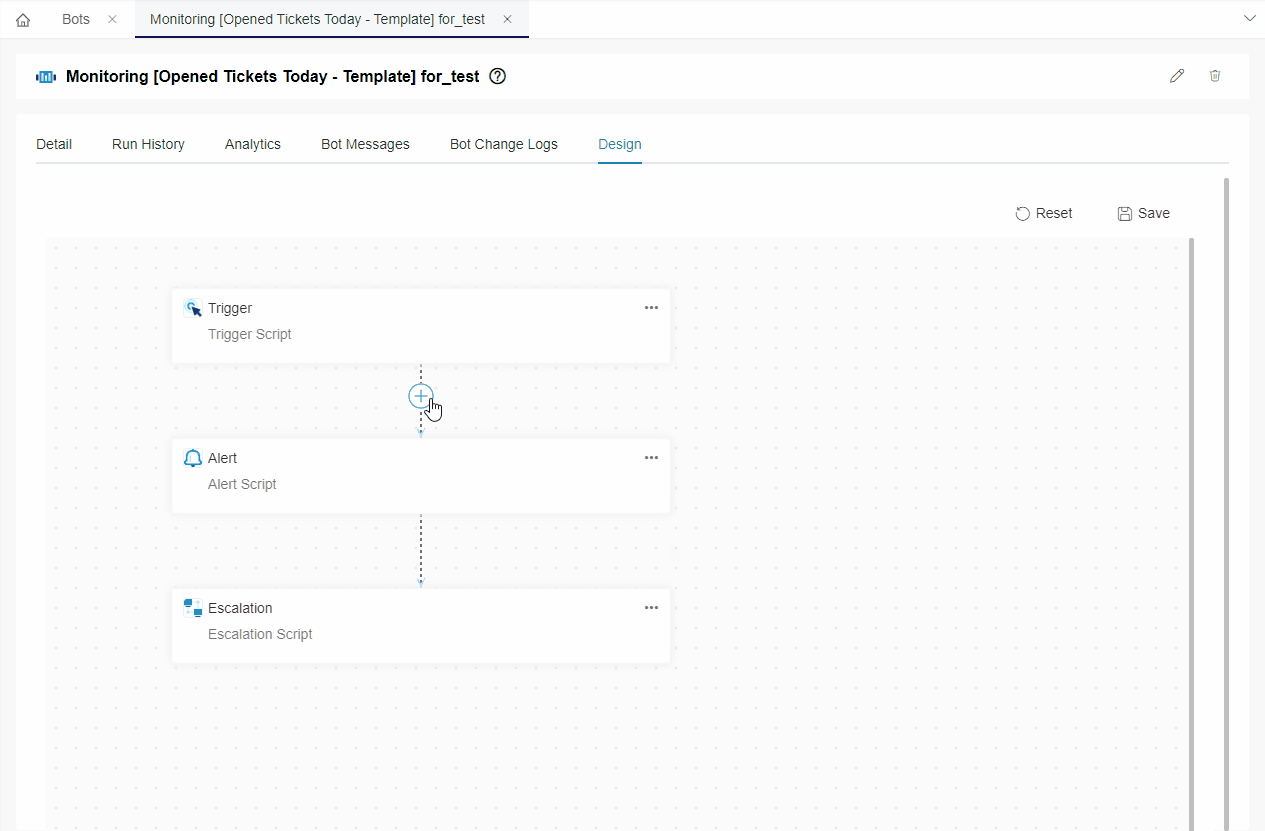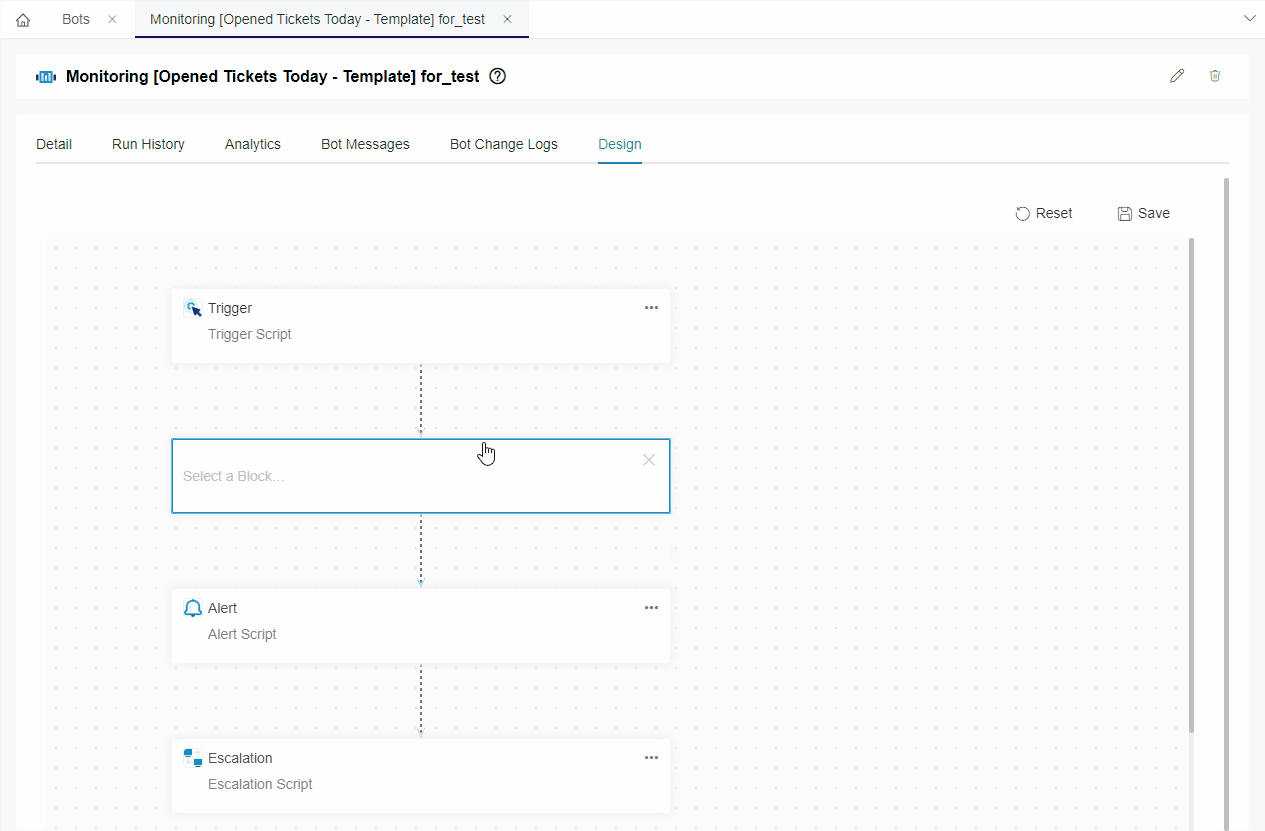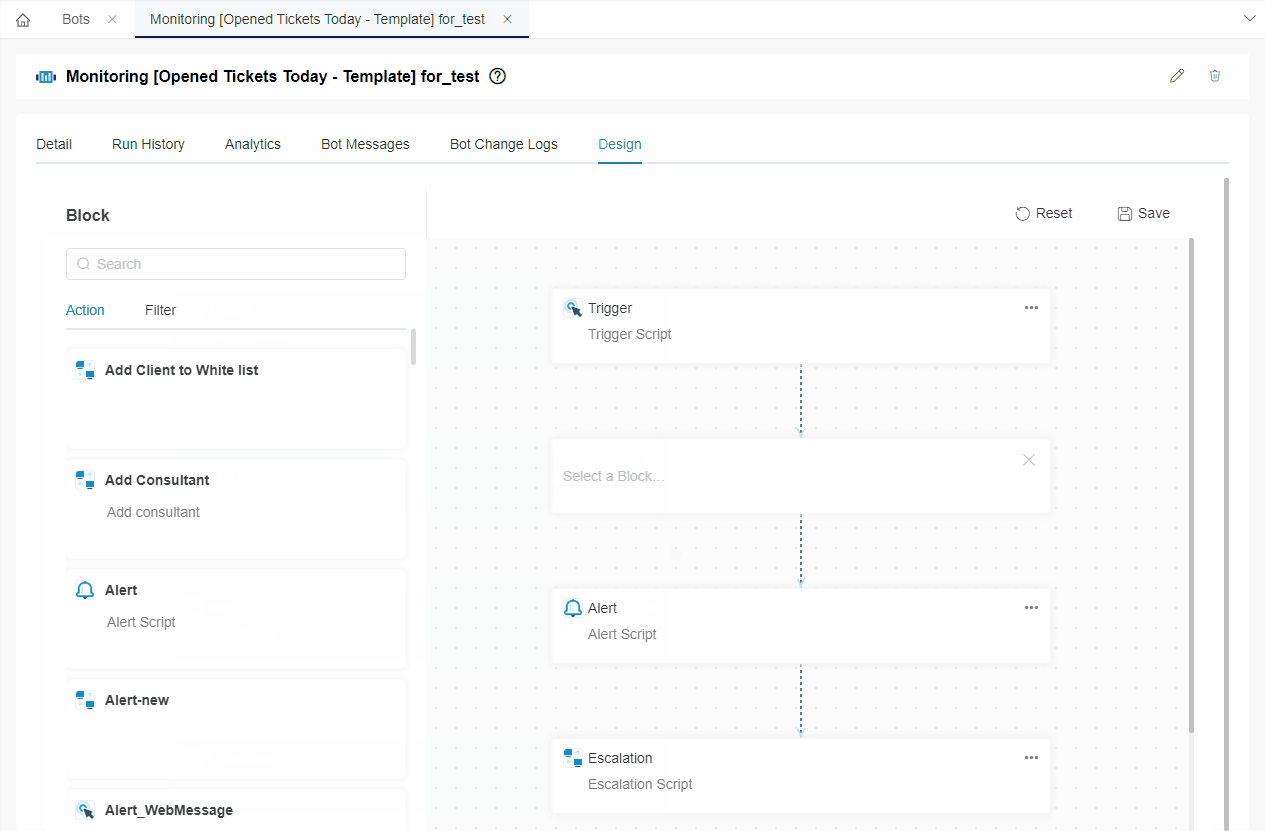
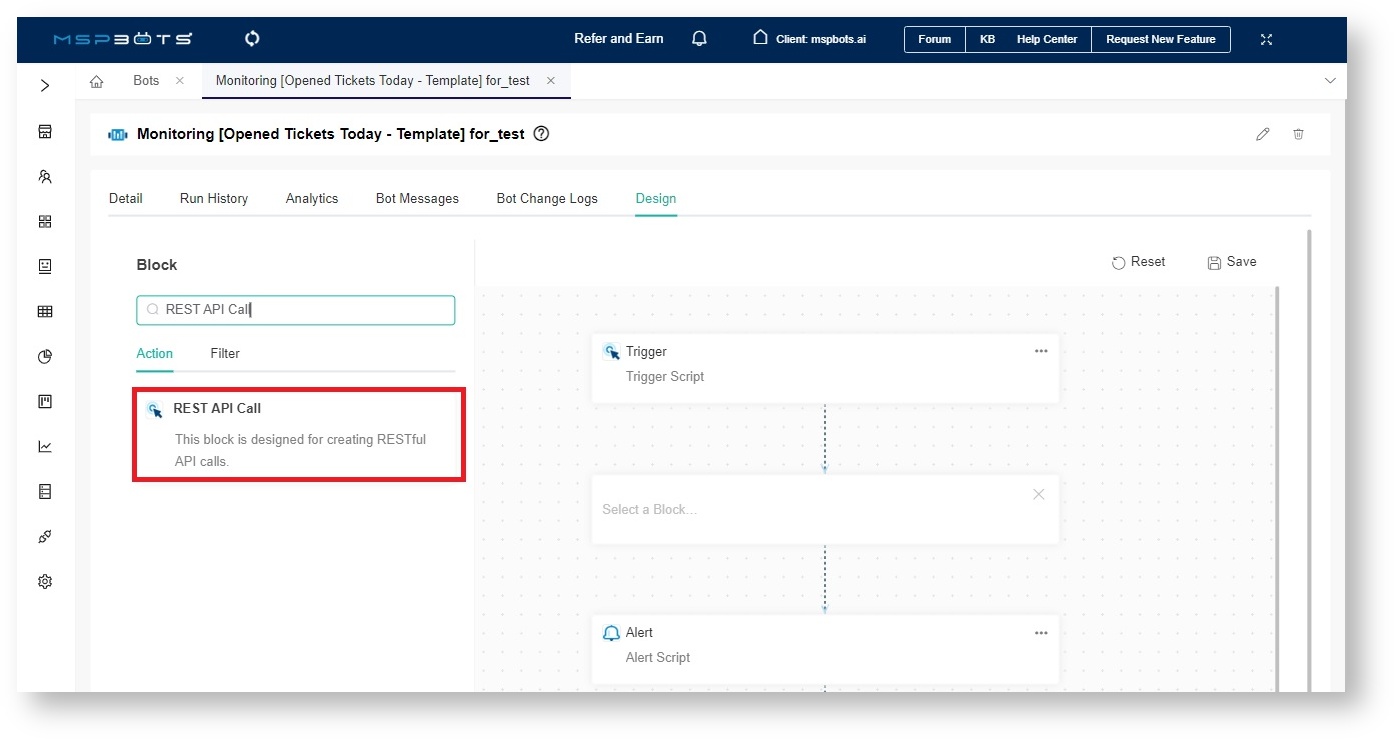
- Type REST API Call in the search bar and click REST API Call.
- Next, hover over the ellipsis for the REST API Call block and select Edit.
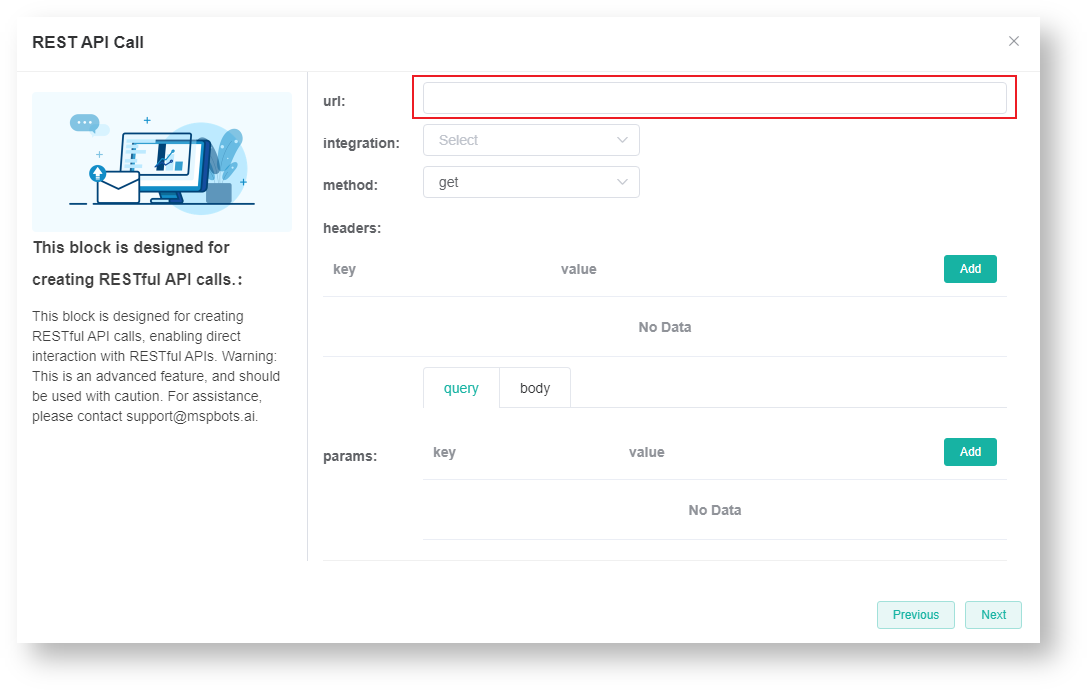
- When the REST API Call window opens, enter the url address that will receive requests.
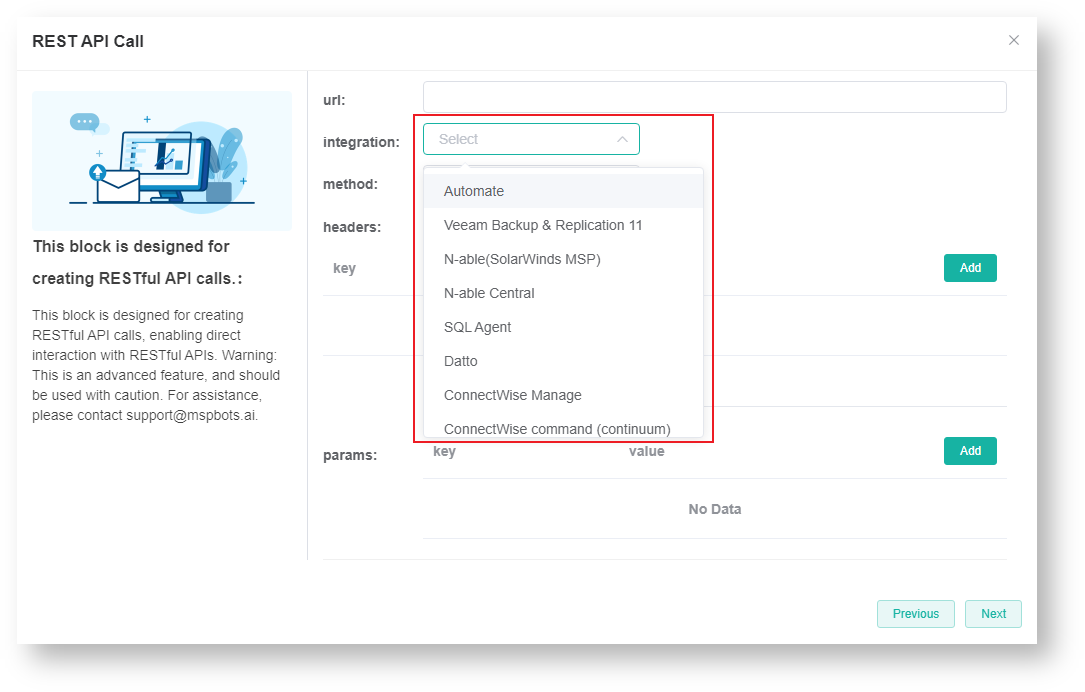
- (Optional) Select an integration.
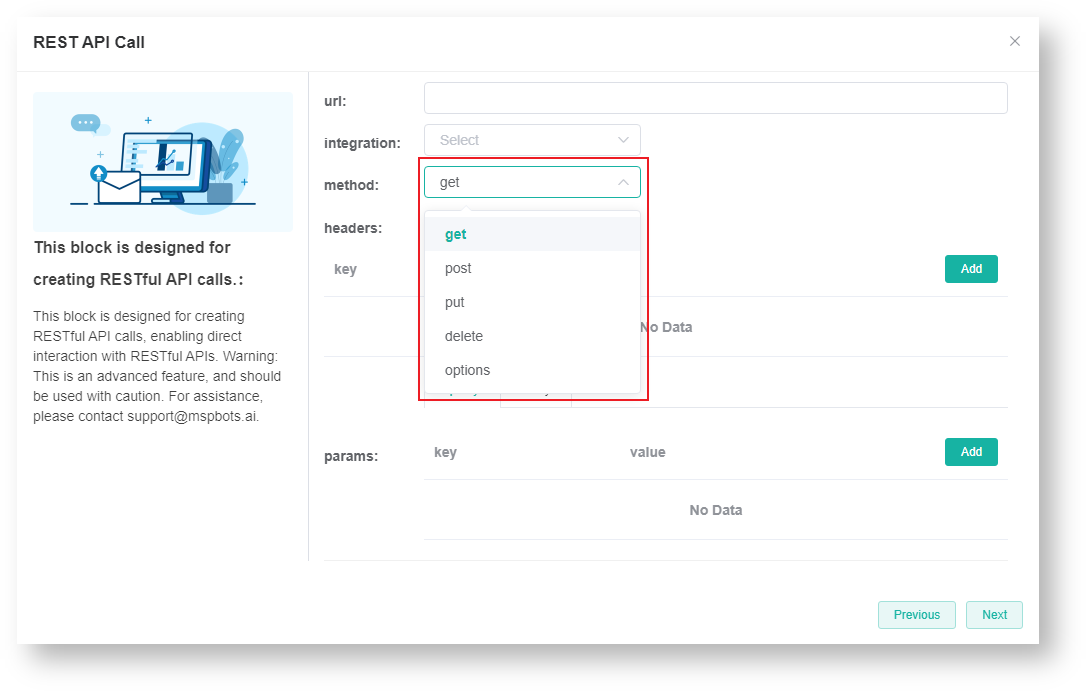
If you are configuring a REST API from an existing integration with MSPbots, select that software from the integration list. Otherwise, please do not configure this parameter. - Select an appropriate HTTP method to use.
- get - Retrieves information from the database without modifying or adding data. The results are consistent regardless of how many operations are performed.
- post: Submits data and adds operations to the server.
- put: Modifies the existing data on the server. This is similar to POST except that it modifies instead of adding.
- delete: Removes a specific resource, like deleting a record in a database.
- options: A pre-check request of the browser to ensure the server accepts the request before sending get, post, put, or delete requests.
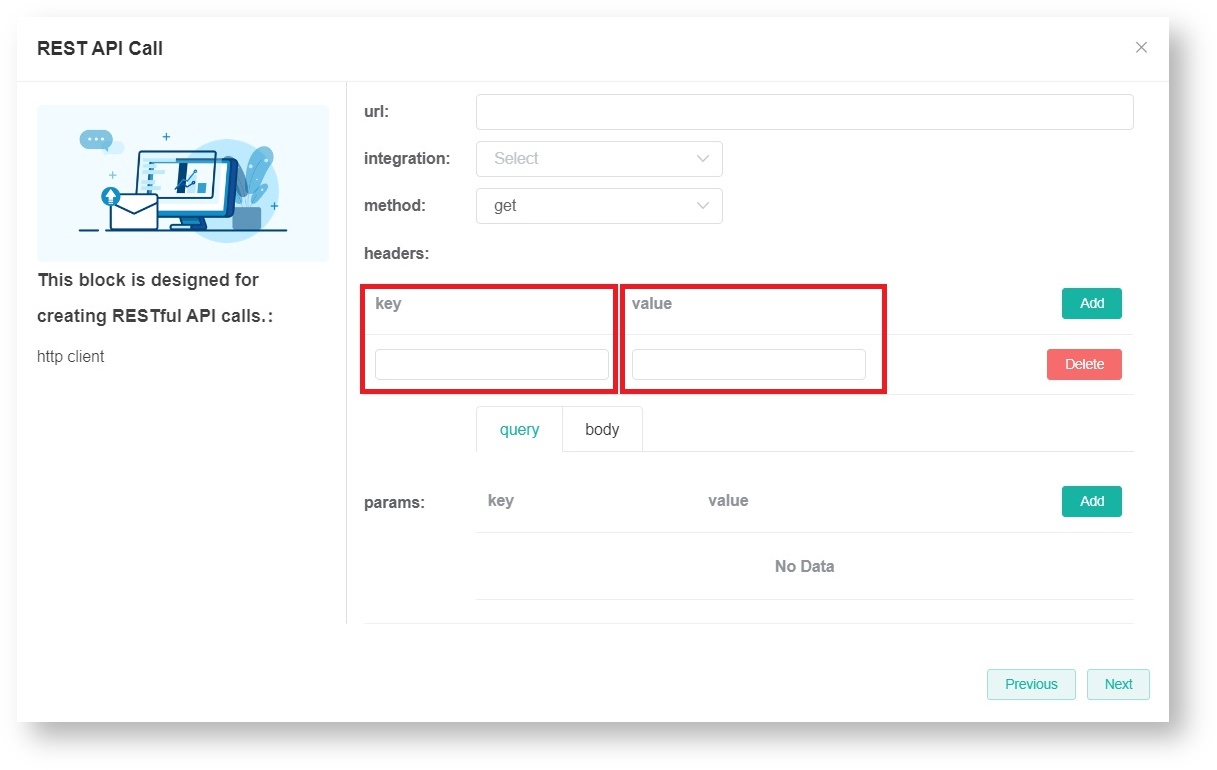
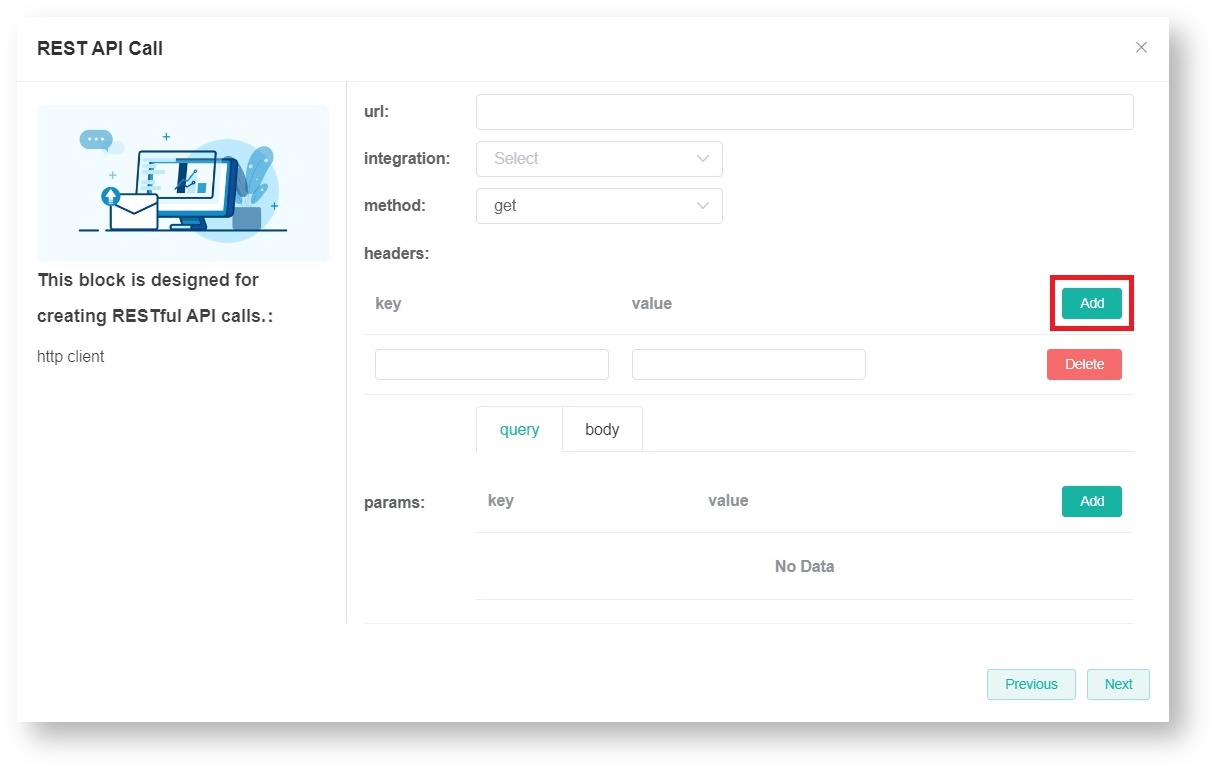
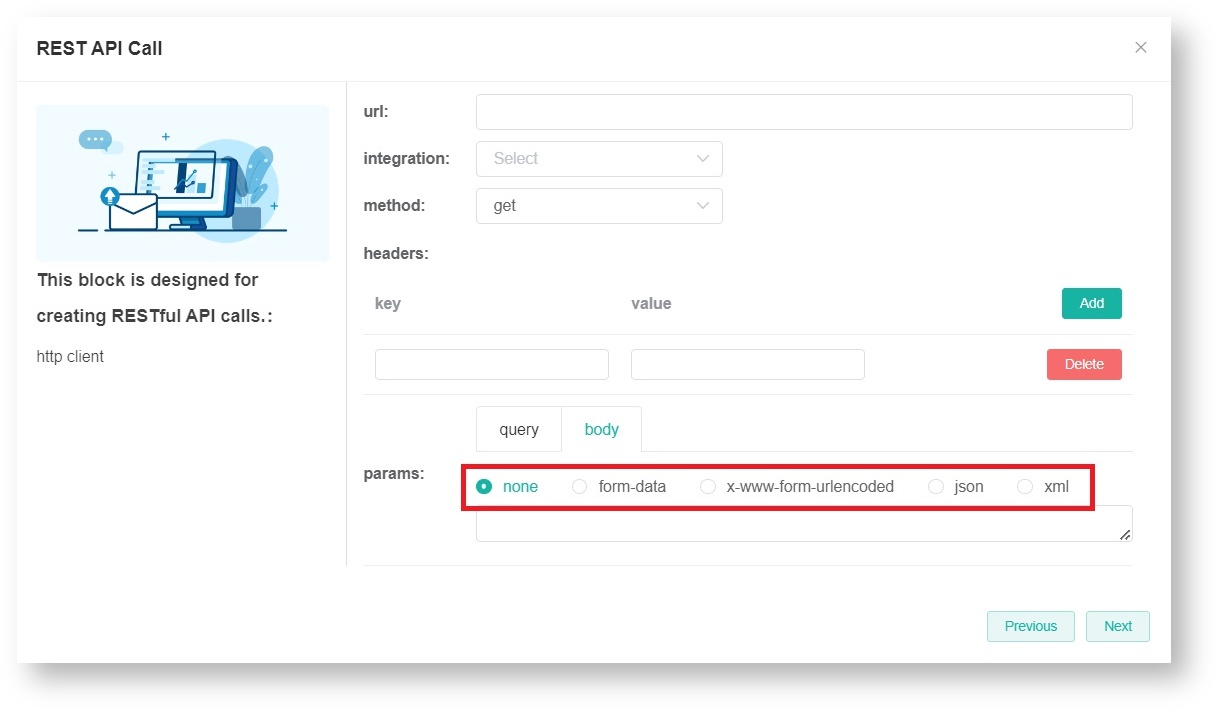
- Next, set up the headers and input the relevant key and value.
Click Add to add more keys and values.
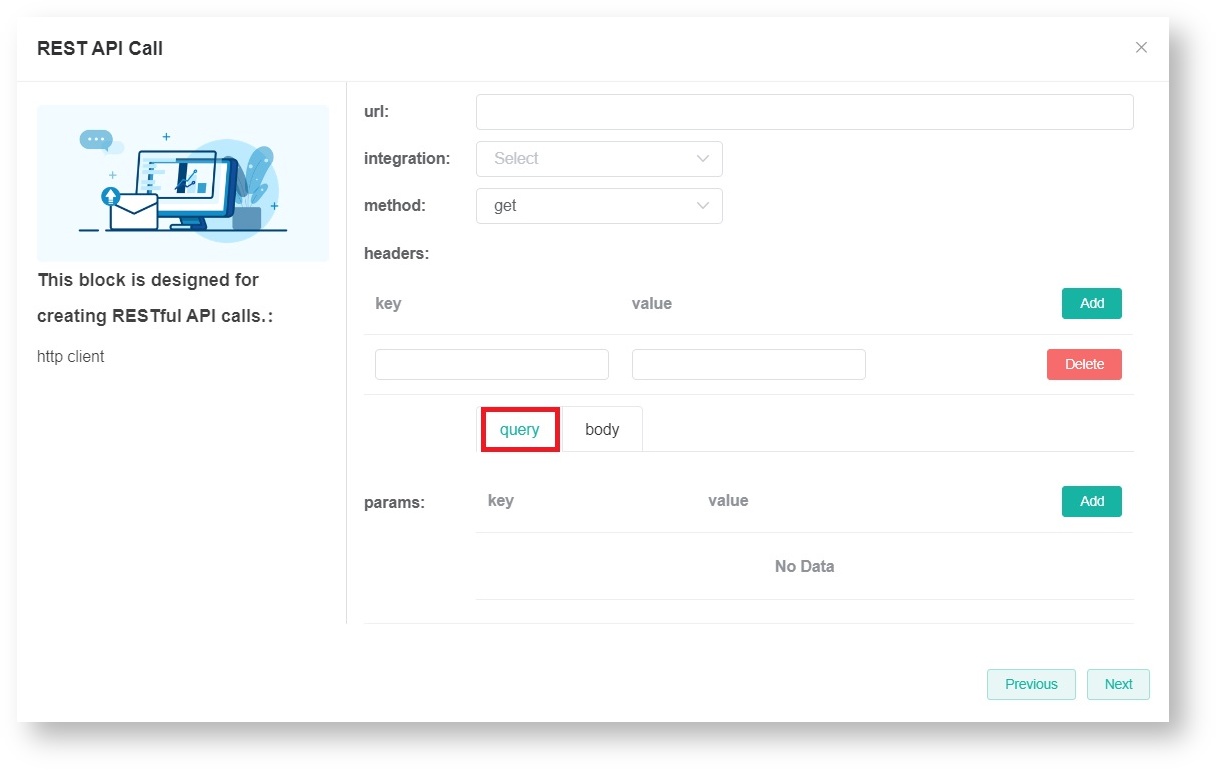
To remove a pair of key and value, click Delete. - Set up the params. Select either the URL query and request body method to pass parameters to the server.
- query
URL query parameters are a way of passing parameters through the URL. In the URL, query parameters usually start with a "?" symbol and are separated by "&" symbols.
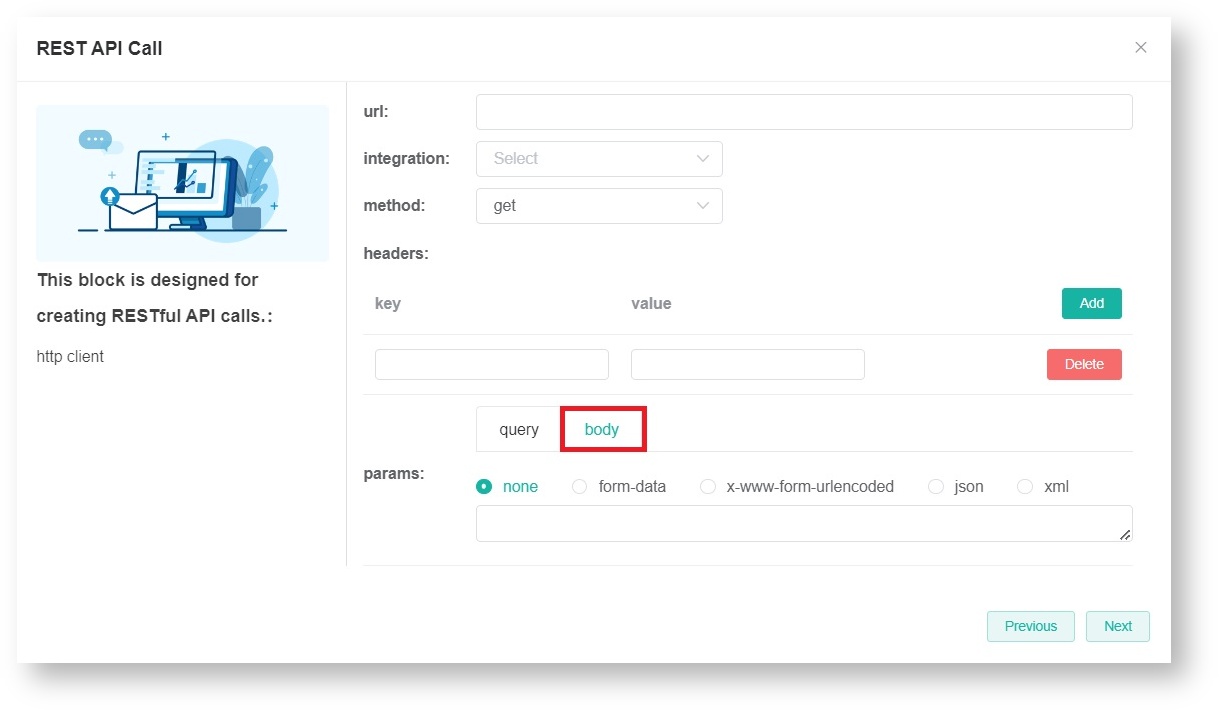
For example: https://www.example.com/path/to/resource?param1=value1¶m2=value2 - body
The request body is an HTTP request with data that is usually part of a POST or PUT request. This data can be in various formats such as JSON, XML, or form data. These parameters are usually used for submitting forms, uploading files, or sending other types of data.
The params available for the request body method are none, form-data, x-www-form-urlencoded, JSON, and XML.
- query
- Click Next to configure any remaining blocks, and click Finish when done.